Okay, let’s be real. When you hear “Federal Reserve,” do your eyes glaze over? Mine used to! But here’s the thing: what the Fed does with interest rates directly impacts your wallet, your job, and the entire economy. It’s not just some abstract concept debated in ivory towers. It’s about how much you pay for a car loan, whether your business expands, and if the stock market keeps chugging along.
So, instead of just reporting on the latest rate hike (or pause!), I want to break down why this stuff matters. We’re going to dive into the nuts and bolts of monetary policy , explore the Fed’s motivations, and, most importantly, figure out what it all means for you. Think of me as your friendly neighborhood Fed decoder. Let’s get started.
The Fed’s Tightrope Walk | Inflation vs. Recession
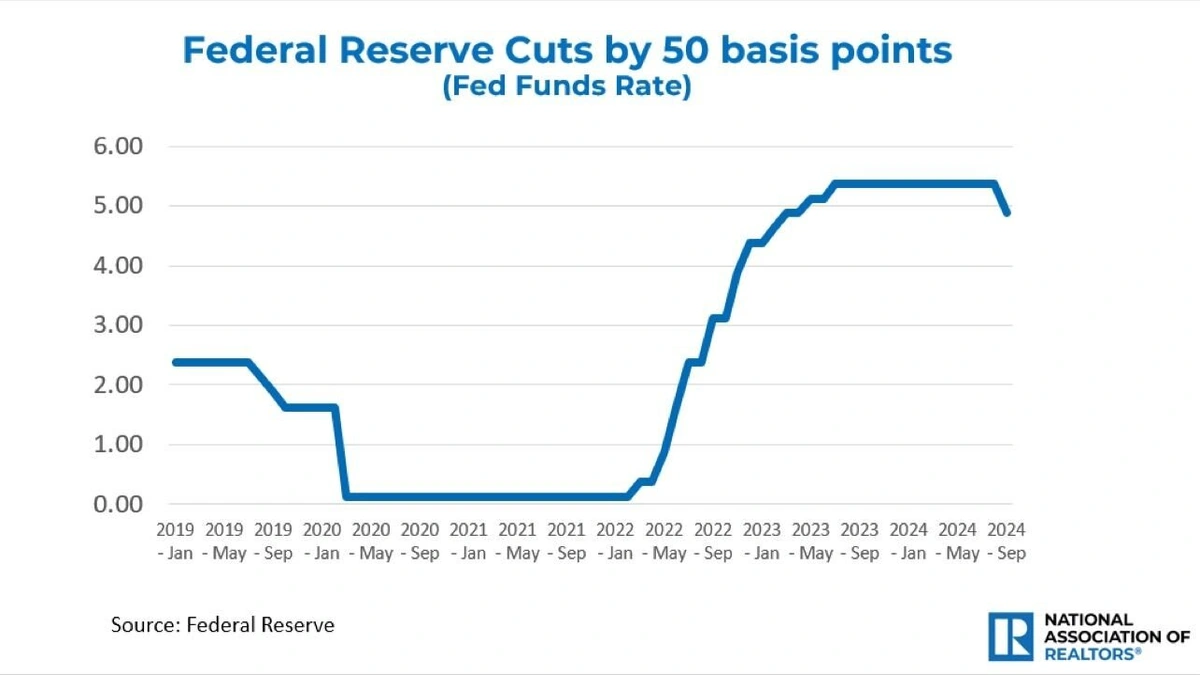
The Federal Reserve, or “the Fed” as everyone calls it, has a dual mandate: to maintain price stability (keep inflation in check) and to promote maximum employment. Sounds simple enough, right? Not so fast. It’s like trying to ride a unicycle uphill in a hurricane.
Here’s the thing: raising interest rates is the Fed’s primary tool to fight inflation. Higher rates make borrowing more expensive, which cools down spending and investment. Less demand means prices theoretically stop rising so quickly. But, and this is a BIG but, higher rates also slow down the economy. Too many rate hikes, and you risk tipping the economy into a recession . It’s a delicate balancing act. What fascinates me is the constant guessing game: are they doing enough? Too much?
So, when you hear about the Fed raising rates, remember they’re trying to control inflation, but also trying to avoid crashing the economy. No pressure, right?
How Federal Reserve Interest Rate Decisions Impact Your Life
This is where it gets personal. Let’s break down how federal reserve interest rate policy affect you, the average American:
- Mortgages: This is the big one for most people. Mortgage rates tend to track the Fed’s moves, though not always perfectly. When the Fed raises rates, expect mortgage rates to rise as well, making it more expensive to buy a home. Refinancing also becomes less attractive. A common mistake I see people make is assuming a quarter-point rate hike won’t matter. It adds up over 30 years!
- Credit Cards: Most credit cards have variable interest rates tied to a benchmark rate, often the prime rate, which moves in tandem with the Fed. So, expect your credit card bills to get a bit fatter after a rate hike. My advice? Pay down that debt!
- Savings Accounts: The upside! Higher rates mean banks will (eventually) offer better interest rates on savings accounts and certificates of deposit (CDs). It’s not a huge windfall, but it’s better than nothing. I initially thought this was straightforward, but then I realized banks are slow to pass these benefits along.
- Business Investment: Businesses borrow money to expand, hire, and invest. Higher rates make those investments more expensive, potentially leading to slower job growth. This is important to keep an eye on.
See? The Fed’s decisions aren’t some abstract concept. They have real-world consequences for your financial well-being.
Beyond the Headlines | Understanding the Fed’s Indicators
The Fed doesn’t just pull interest rate decisions out of a hat. They rely on a ton of economic data to guide their hand. Understanding these indicators can give you a better sense of where the Fed might be heading.
- The Consumer Price Index (CPI): This measures changes in the prices of a basket of goods and services that consumers buy. It’s the primary gauge of inflation.
- The Unemployment Rate: This measures the percentage of the labor force that is unemployed. A low unemployment rate generally indicates a strong economy.
- Gross Domestic Product (GDP): This measures the total value of goods and services produced in the economy. It’s a key indicator of economic growth.
- The Personal Consumption Expenditures (PCE) Price Index: This is the Fed’s preferred measure of inflation, as it accounts for changes in consumer behavior.
So, when you read about these indicators in the news, remember they’re not just numbers. They’re the data points that the Fed is using to make decisions that will affect your life. As per the guidelines mentioned in the information bulletin , the Fed also monitors global economic conditions.
Navigating Uncertainty: What the Future Holds for Interest Rates
Let’s be honest: predicting the future of interest rates is like predicting the weather six months from now. There are simply too many variables. Geopolitical events, unexpected economic shocks, and even changes in consumer sentiment can all throw a wrench into the Fed’s plans. But, we can make some educated guesses based on current trends and the Fed’s own communications.
Currently, the big question is whether the Fed will continue to raise rates aggressively, pause its rate hikes, or even start cutting rates. This depends largely on whether inflation continues to cool down. A common mistake I see people make is panic-selling their investments when rates rise. Consider a long-term strategy.
Remember, the Fed’s goal is to achieve a “soft landing” – bringing inflation down without causing a recession . Whether they can pull it off remains to be seen. Keep an eye on those economic indicators, stay informed, and don’t make rash decisions based on short-term market fluctuations.And, most importantly, stay calm.
FAQ: Understanding Federal Reserve Interest Rate Policy
What exactly is the federal funds rate?
It’s the target rate that the Federal Reserve wants banks to charge one another for the overnight lending of reserves. This influences other interest rates throughout the economy.
How often does the Fed meet to discuss interest rates?
The Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC), which sets interest rate policy, meets about eight times a year.
What if inflation stays high despite the Fed’s actions?
The Fed may have to raise interest rates even further, potentially increasing the risk of a recession . This is the big fear right now.
Can the Fed directly control mortgage rates?
No, but the Fed’s actions strongly influence mortgage rates. Other factors, such as investor demand for mortgage-backed securities, also play a role.
Why does the Fed focus so much on inflation?
High inflation erodes purchasing power, creates economic uncertainty, and can lead to financial instability. The Fed wants to keep prices stable to promote long-term economic growth.
inlation rate is an important thing to understand.
Here’s the thing… understanding the Fed isn’t about becoming an economist. It’s about understanding how the decisions made in those boardrooms can impact your life. It’s about being informed and making smart financial choices. And hopefully, after reading this, you feel a little more empowered to do just that.




